Taylor & Wells 12 Roundtree Euro Pillow Top Mattress Reviews
Taylor diagrams provide a visual framework for comparison a suite of variables from one or more than test information sets to 1 or more reference data sets. Commonly, the examination information sets are model experiments while the reference information set up is a control experiment or some reference observations (eg, ECMWF Reanalyses). Generally, the plotted values are derived from climatological monthly, seasonal or almanac means. Because the different variables (eg: precipitation, temperature) may have widely varying numerical values, the results are normalized past the reference variables. The ratio of the normalized variances indicates the relative amplitude of the model and observed variations.
For the classic Taylor Diagram (Karl, 2005), the pertinent statistics are the weighted centered pattern correlation(due south) (pattern_cor) and the ratio(due south) of the normalized root-mean-square (RMS) differences betwixt 'test' dataset(s) and 'reference' dataset(s). An additional bias statistic, developed by R. Neale (NCAR), may added to the classic Taylor Diagram. See taylor_7b below.
NCL V6.5.0 contains a function, taylor_stats , which creates the statistics needed for the taylor diagram: pattern_correlation, ratio and bias. Optionally, additional statistics can be returned. Prior to the release of NCL 6.5.0, the taylor_stats office may exist downloaded from here.
Reference:
Taylor, K.Due east. (2005): Taylor Diagram Primer: A brief iv-page overview which summarizes the important aspects of these useful plots. --- Taylor, K.Due east. (2001): Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram JGR, vol 106, no. D7, 7183-7192, April 16, 2001. Gleckler, P. J., K. E. Taylor, and C. Doutriaux (2008): Performance metrics for climate models J. Geophys. Res., 113, D06104 Baker, N.C., Taylor, P.C (2016): A Framework for Evaluating Climate Model Performance Metrics Journal of Climate, 2016, 29, 5, 1773.
The following examples employ taylor_diagram.ncl or taylor_diagram_cam.ncl to generate the groundwork upon which the normalized statistics are plotted. The advantage of using the normalized version of the Taylor diagram is that variables with widely varying variances tin can be viewed on 1 figure.
The archetype taylor_diagram function is prototyped as follows:
function taylor_diagram ( wks:graphic\ ; pre-created workstation , RATIO[*][*]:numeric \ ; ratios , CC[*][*]:numeric \ ; pattern correlations: range 0-ane , rOpts:logical) ; scalar to which attributes are assigned
The version that includes the bias is prototyped equally:
function taylor_diagram_cam ( wks:graphic\; pre-created workstation , RATIO[*][*]:numeric \ ; ratios , CC[*][*]:numeric \ ; blueprint correlations: range 0-ane , BIAS[*][*]:numeric \ ; rlative bias (%) , rOpts:logical) ; scalar to which attributes are assigned
The arguments are:
- RATIO[*][*]: ratio of the standardized variances
- CC[*][*]: pattern correlations: range 0-to-1
- BIAS[*][*]: relative bias (%): See taylor_8
- rOpts: options
The RATIO, CC and BIAS arguments are 2 dimensional. The left dimension refers to the number of exam data sets used (eg: model experiments and/or observational). The right dimension holds the actual values to exist plotted. If only one comparison dataset is used, the ratio, cc and bias are scalars. to plot, the user must create a ii dimensional array prior to calling the office. EG:
CC = conform_dims( (/1,1/), cc) RATIO = conform_dims( (/ane,one/), ratio) BIAS = conform_dims( (/1,i/), bias)
The process taylor_metrics_table.ncl can be used to create a table containing a specified statistic. See taylor_{7,8}.
process taylor_metrics_table (mfname[one]:cord \ ; plot name ,varNames[*]:cord \ ; variable names ,cases[*]:cord \ ; instance (model) names ,seasons[*]:string \ ; season names ,values[*][*][*]:numeric \ ; 3d array w values ,topt:logical ) ; table options
By default, the taylor diagram functions can handle upwards to x variable comparisons. Unlike colors and markers are used to differentiate between different models/cases. The 10 default colors and markers are:
Markers = (/ 4, half-dozen, 8, 0, 9, 12, 7, two, 11, 16/) ; Marker Indices Colors = (/ "cherry" , "blue" , "green" , "cyan" , "orange" \ , "turquoise", "chocolate-brown", "xanthous", "purple", "blackness" /)
The markers and colors can readily exist changed past the user.
The taylor_diagram plot options are activated by setting the option argument, (say) "opt", to True and setting diverse attributes. The user specified aspect options include:
opt = Truthful ; taylor diagram with options opt@tiMainString = "......" ; title opt@Markers = (/ ... /) ; markers opt@Colors = (/ ... /) ; colors opt@caseLabels = (/ ... /) ; case Labels opt@varLabels = (/ ... /) ; variable Labels opt@caseLabelsFontHeightF = ; caseLabels size [default=0.12 ] opt@varLabelsFontHeightF = ; varLabels size [default=0.013 ] opt@varLabelsYloc = ; Move location of variable labels ; [default=0.45] opt@gsMarkerSizeF = ; marker size [default=0.0085] ; Groundwork options opt@stnRad = (/ ... /) ; additional standard radii opt@ccRays = (/ ... /) ; correlation rays opt@centerDiffRMS = True ; RMS 'circles' opt@ccRays_color = "LightGray" ; default is black opt@centerDiffRMS_color = "LightGray" ; default is black ; OTHER recognized options opt@taylorFrame = False ; practice not advance frame [default is True]
The following examples illustrate the most usually used options.
The taylor_metrics_table options are activated by setting the choice argument, (say) opt=Truthful and setting various attributes. The user specified aspect options include:
opt = True ; taylor metric table with options opt@tiMainString = "......" ; title [default="CAM METRICS"] ; make roughly the same length
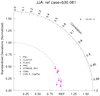
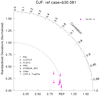
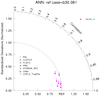
 taylor_7.ncl: A simple processing script that compares a unmarried test model versus a reference (command) case. The 'classic' Taylor diagram quantities (pattern correlations and ratios) were calculated using taylor_stats . The taylor_diagram.ncl plotting function is used. For convenience, The annual [ANN] and seasonal [eg: JJA, DJF] quantities are derived from the monthly climatologies.
taylor_7.ncl: A simple processing script that compares a unmarried test model versus a reference (command) case. The 'classic' Taylor diagram quantities (pattern correlations and ratios) were calculated using taylor_stats . The taylor_diagram.ncl plotting function is used. For convenience, The annual [ANN] and seasonal [eg: JJA, DJF] quantities are derived from the monthly climatologies.
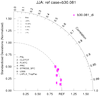
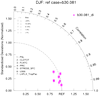
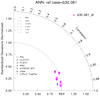 taylor_7b.ncl: Like to the taylor_7 instance except the relative bias is plotted. The pertinent statistics are calculated using taylor_stats . This requires using the taylor_diagram_cam.ncl plotting office.
taylor_7b.ncl: Like to the taylor_7 instance except the relative bias is plotted. The pertinent statistics are calculated using taylor_stats . This requires using the taylor_diagram_cam.ncl plotting office.
carterlithatinquir.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.ncl.ucar.edu/Applications/taylor.shtml
0 Response to "Taylor & Wells 12 Roundtree Euro Pillow Top Mattress Reviews"
Post a Comment